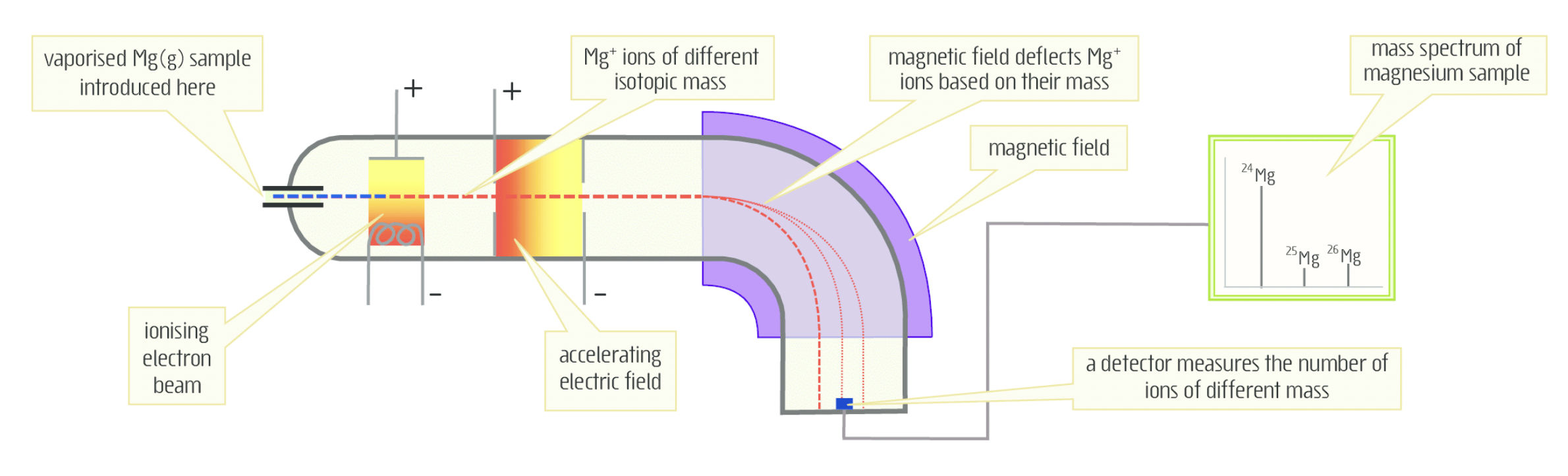
- Mass spectrometer is a tool used to determine relative molecular mass and structure of complex organic compounds.
- Vaporisation: Element is turned into gas by heating in a vacuum and passed to mass spectrometer.
- Ionisation: Passes through a high energy electron beam where collisions cause gas particles to lose one electron to form 1+ ions (few +2 ions may form)
- Acceleration: accelerated into an electric field, deflected by the field and move in circular paths depending on masses. lower mass = more deflection
- Detection: detector measures the intensity and radius of deflection of beams, measuring the isotope abundance, displayed as a mass spectrum.