- pure substances have a fixed or constant composition
- cannot be separated by physics means
- well defined physics properties, e.g:
- melting point
- boiling point
- hardness
- density
- colour
- have constant chemical properties
mixtures §
- contains two or more diff substances, in proportions that can vary
- properties vary with composition, depend on the identity and amounts of constituents
- properties of individual constituents can be used to separate the mixture
separating mixtures §
- sieving
- filtration (diagram)
- use to separate heterogeneous mixtures composed of solids and liquids
- uses a porous barrier to separate the solid from the liquid.
- smaller particles of liquid passes through leaving the solid in the filter paper
- decanting
- done to separate particulates from a liquid by allowing the solids to settle to the bottom of the mixture and pouring off the particle-free part of the liquid.
- another method is to allow two immiscible liquids to separate and the lighter liquid is poured off.
- separating funnel is better than decanting
- use of separation funnel (diagram)
- dehydrating agent to remove water
- something filtered using funnel is called filtrate
- distillation (diagram)
- you need to be very careful and selective
- a question might ask for you to choose a method
- if this is the case, identify if substances is homogenous or heterogenous
- distillation works for homogenous, LIQUID homogenous mixtures
- if it is simple distillation, there must be a NOTICEABLE difference in boiling point.
- eg water and ethanol works for distillation
- you can use heating mantle instead of bunsen burner
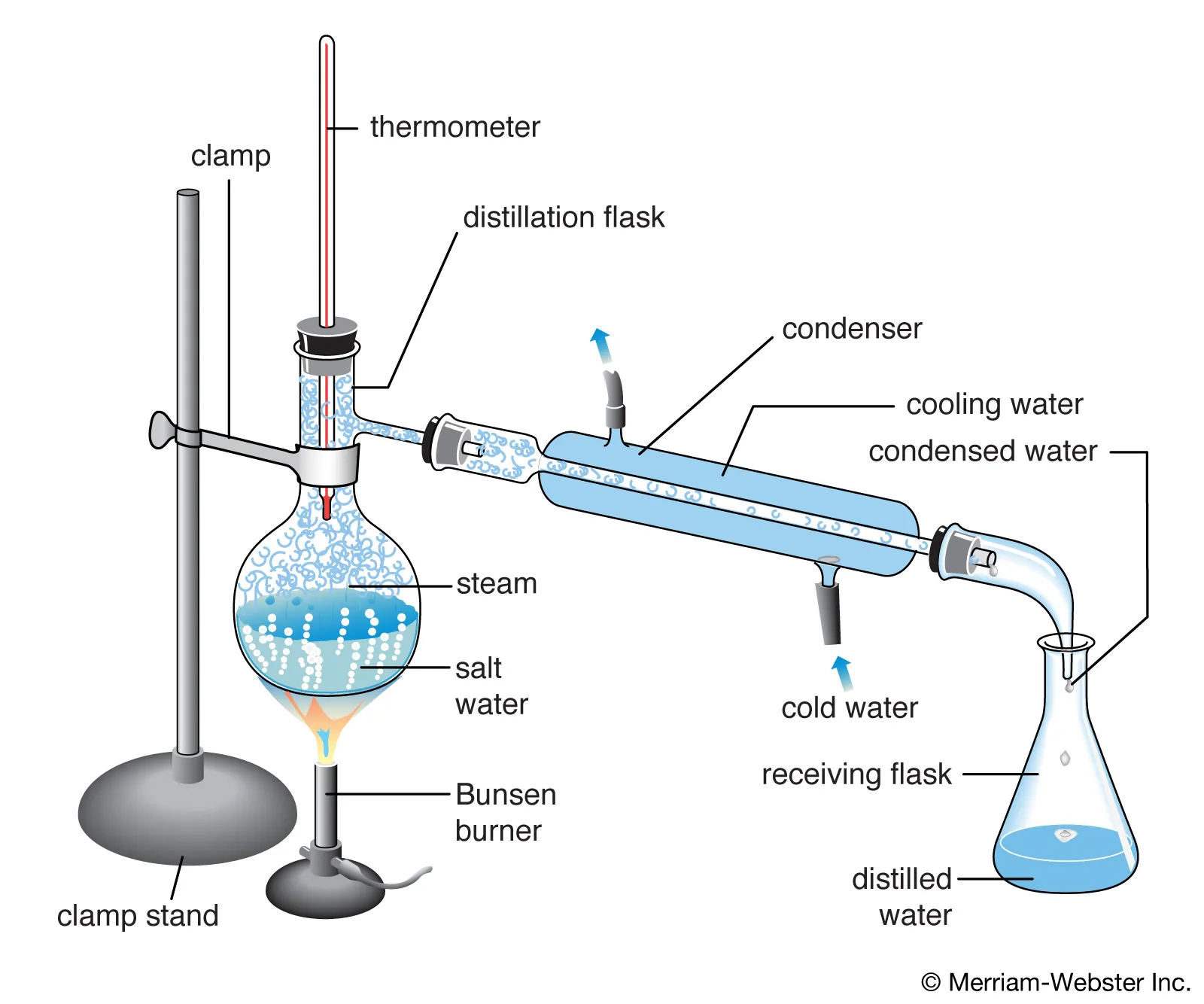
- you should be able to label this (no need to draw diagram)
- not incl: water outlet label, distillate label
- fractional distillation (basic diagram)
- when the boiling point is too close together for normal distillation.
- more than 2 things to be separated
- electrostatic attraction
- magnetic susceptibility
- vaporisation
- crystallisation
- chromatography
- centrifuging
- evaporating
- dissolving
- sieving
- a porous material is used to separate particles of different sizes.
- method is most commonly used to effect gross separations, as of liquids from suspended crystals or other solids.
- to accelerate filtration, pressure usually is applie.
- a series of sieves is stacked, with the screen of largest hole size at the top.
- flotation
homogenous materials §
- have uniform compositions throughout
- include all pure substances (elements and compounds) and some mixtures.
- the only kind of mixture that is homogenous is a solution, eg: salt water.
heterogeneous materials §
- materials are non-uniform - you can see differences from one section to another
- the constituents are physically separated, eg: in a different phase
- examples include
- granite (mixture of mineral grains)
- milk (fat globules suspended in water)
- toothpaste (solid particles suspended in liquid)
