redox questions §
- redox reactions involve transfer of one or more electrons from one species to another.
electrochemistry in action! §
- what is electrolysis
- a process where electricity is used to make a chemical change happen that wouldn’t happen otherwise. (non-spontaneous)
- types of galvanic cells
- primary cell, secondary cell, fuel cell.
- primary cell definition
- non-rechargeable galvanic cells
- contains fixed amount of oxidant and reductant, which once consumed cannot be replaced/regenerated.
- secondary cell definition
- how are secondary cells recharged?
- applied dc voltage forcing current through cell in opposite direction to that it spontaneously reacted during discharge.
- describe the process of recharging
- electrolysis where electrical energy is used to force the spontaneous discharge reactions to be reversed, and in the process, regenerate oxidant and reductant originally present in the charged cell.
- tldr; reverses the original reactions and turns the products back into its original reactants.
- drawbacks of secondary cells?
- there is a limit to number of recharge cycle,
- as electrodes becomes physically degraded over time, and no longer able to be recharged
- what are fuel cells.
- oxidants and reductant are continously being fed into the cell.
- the cell is a combustible substance: fuel.
- examples of fuel cells
- hydrogen, methane, methanol.
- what is usually oxidant of fuel cell
- advantages of fuel cells
- very long life
- theoretically operate without limit as long as the oxidant and reductant are supplied into the cell.
- what is a dry cell
- simplest, most inexpensive of primary cells (non-rechargeable cells)
- disadvantages of dry cell
- produces max voltage of 1.5 V
- voltage produced slowly decreases over lifetime of cell.
- very low energy to mass ratio (energy density)
- cannot be recharged (primary cell)
- ammonium ions cause zinc anode to dissolve forming Zn2+ ions, thus it has low shelf life (~1 year)
- advantages of dry cell
- inexpensive
- ideal for use in flashlight, portable radios and calculators where low currents are required and decreasing voltage is not an issue.
- materials used in dry cell (Zn, MnO2, Nh4Cl and C) pose negligible environmental impact. spent dry cells are considered non-hazardous waste and can be disposed of in normal household.
- materials used in dry cell
- Zinc Zn
- Manganese Dioxide MnO2
- Ammonium Chloride NH4Cl
- Carbon C
- types of primary cells
- dry cells
- alkaline cell
- silver oxide button cells
- lithium cells
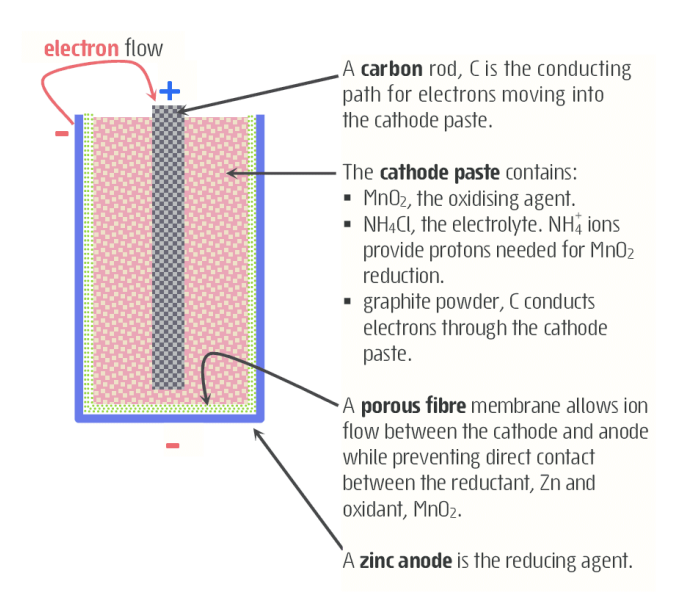
- diagram of dry cell
- oxidation half reaction for dry cell
- reduction half reaction for dry cell
- 2MnO2 (s) + 2NH4+ (aq) + 2e- -> Mn2O3 (s) + 2NH3 (aq) + H2O (l)
- net reaction for dry cell
- 2MnO2 (s) + 2NH4+ (aq) + Zn (s) -> Zn2+(aq) + Mn2O3 (s) + 2NH3 (aq) + H2O (l)
- what is reducing agent in alkaline cell
- what is the oxidising agent in alkaline cell
- difference dry cell and alkaline cell, and impact
- instead of ammonium chloride electrolyte, it uses potassium hydroxide.
- considerable improves shelf life by eliminating effect of acidic ammonium ions that ultimately dissolve zinc anode of dry cell.
- zinc anode is powdered zinc, instead of zinc foil in dry cell.
- provides more surface area for chemical reactions to take place compared to foil. lowers internal resistance of cell (?)
- greater mass of reductant, Zn and oxidant, MnO2 than dry cell of similar size.
- higher energy density and longer operating life.
- oxidation half reaction in alkaline cell
- Zn (s) + 2OH- (aq) -> ZnO (s) + H2O (l) + 2e-
- reduction half reaction in alkaline cell
- 2MnO2(s) + H2O(l) + 2e- -> Mn2O3 (s) + 2OH- (aq)
- overall redox reaction:
- Zn(s) + 2MnO2(s) -> ZnO(s) + Mn2O3 (s)
- where is alkaline cells used
- higher current flow devices
- toys, portable radios, cd players, electronic games & torches.
- benefits of alkaline cells
- minimal environmental impact (same as dry cells)
- considered non-hazardous waste.
- disadvantages
- disposed in normal household waste stream.
- no economic process for recycling the materials in these cells.
SILVER OXIDE BUTTON CELLS
LITHIUM CELLS
SECONDARY CELLS BLA BLAH